2026 BECE Integrated Science Master Revision: Human Systems and Chemical Bonding

To excel in the 2026 BECE Integrated Science exam, candidates must have a firm grasp of the biological systems that sustain life and the chemical principles that govern matter. Following the Common Core Programme (CCP), this revision guide uses interactive notes to simplify complex topics like Digestion, Respiration, Circulation, and Ionic Bonding.
Below is your comprehensive revision toolkit. Use these notes to study, and then challenge yourself with the practice questions provided.
2026 BECE Integrated Science Master Revision: Human Systems and Chemical Bonding
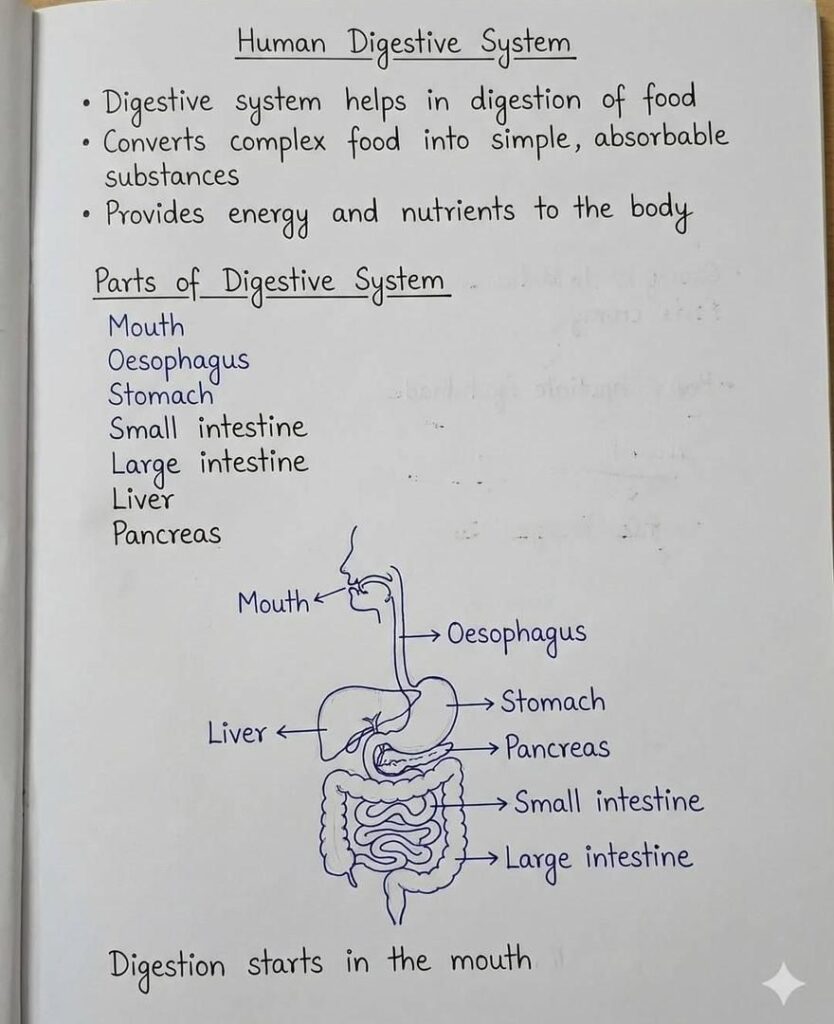
1. Nutrition and the Human Digestive System
Nutrition is the foundation of life, providing the energy required for growth and repair. Digestion is the specific process of breaking down complex food into simple soluble substances that the body can absorb.
Key Revision Points:
-
Types of Nutrition: Organisms are either Autotrophic (make own food, e.g., Green plants) or Heterotrophic (depend on others, e.g., Humans, Fungi).
-
The Process: Involves Ingestion → Digestion → Absorption → Assimilation → Egestion.
-
Organ Functions:
-
Mouth: Chewing and mixing with saliva.
-
Stomach: Primary site for protein digestion.
-
Small Intestine: Completion of digestion and nutrient absorption.
-
Large Intestine: Water absorption.
-
-
End Products: Carbohydrates turn into Glucose, Proteins into Amino acids, and Fats into Fatty acids + Glycerol.
2026 BECE Integrated Science Master Revision: Chemical Bonding: Metals and Non-Metals
Understanding how elements interact is key to Chemistry. Ionic bonds are formed by the complete transfer of electrons between atoms.
Mastering Ionic Bonds:
-
Metals: Lose electrons to become positive ions (Cations).
-
Non-metals: Gain electrons to become negative ions (Anions).
-
Electrostatic Force: The strong attraction between these oppositely charged ions holds the ionic compound together.

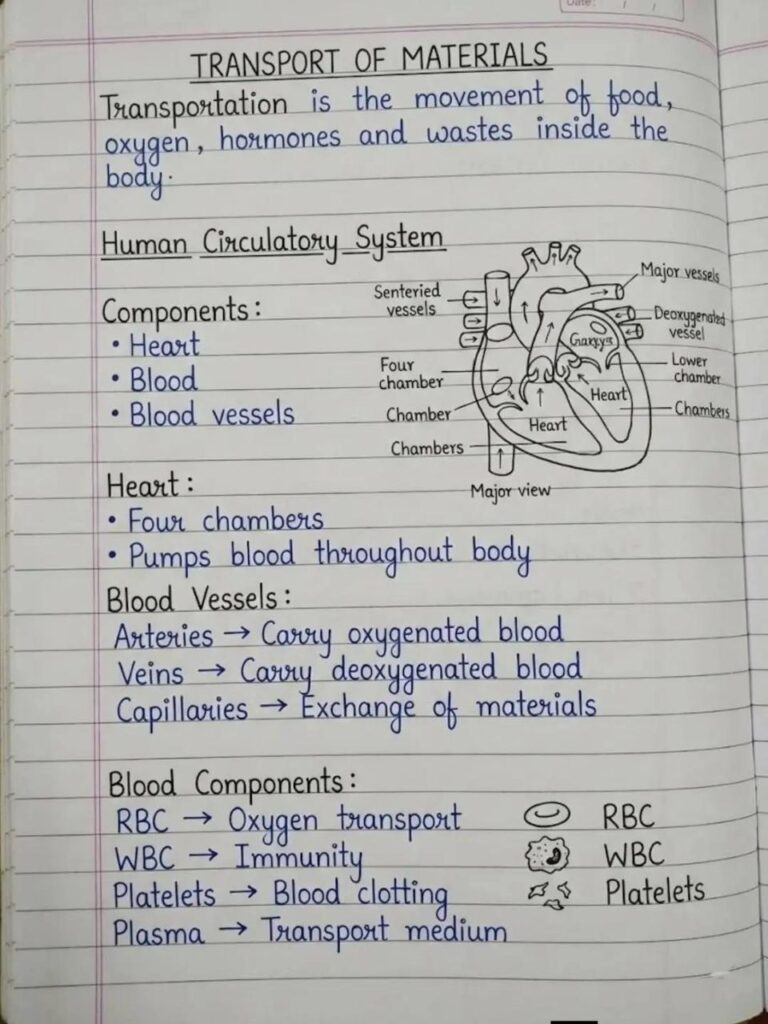
3. 2026 BECE Integrated Science Master Revision: Transportation: The Circulatory System
Transportation is the movement of nutrients, oxygen, hormones, and wastes inside the body.
System Components:
-
The Heart: A four-chambered organ that pumps blood throughout the body.
-
Blood Vessels: Arteries (carry oxygenated blood), Veins (carry deoxygenated blood), and Capillaries (site of material exchange).
-
Blood Cells: RBCs for oxygen transport, WBCs for immunity, and Platelets for blood clotting.

2. Respiration: Releasing Energy
Respiration is the chemical process of breaking down food (glucose) to release energy in the form of ATP.
Comparison of Types:
-
Aerobic Respiration: Uses oxygen for the complete breakdown of glucose, producing $CO_2$, $H_2O$, and high energy.
-
Anaerobic Respiration: Occurs without oxygen. In human muscles, it produces Lactic Acid, while in yeast, it produces Alcohol and $CO_2$.

Revision Tips for Students
-
Visualize the Systems: Use the diagrams to trace the path of food through the gut or blood through the heart.
-
Bonding Logic: Remember that Metals = Givers (+) and Non-Metals = Takers (-) in ionic bonding.
-
End Products: Master the transformation of nutrients, as these are frequent targets for BECE Section A questions.
Section 1: Nutrition & the Digestive System
Q1: Define nutrition according to the biological process.
View Answer
Nutrition is the process by which organisms take in food and utilize it for energy, growth, and repair.
Q2: What are the two main types of nutrition?
View Answer
1. Autotrophic Nutrition. 2. Heterotrophic Nutrition.
Q3: Name the substances used by green plants to make their own food.
View Answer
Sunlight, Carbon Dioxide (CO2), and water.
Q4: Give an example of a parasitic heterotroph.
View Answer
Cuscuta (Dodder plant).
Q5: What is the biological definition of digestion?
View Answer
Digestion is the process of breaking down complex food into simple soluble (absorbable) substances.
Q6: Where exactly does digestion begin in humans?
View Answer
In the mouth.
Q7: Name the three main digestive glands.
View Answer
1. Salivary glands. 2. Liver. 3. Pancreas.
Q8: What is the primary function of the large intestine?
View Answer
Absorption of water.
Q9: State the end product of carbohydrate digestion.
View Answer
Glucose.
Q10: What are the two end products of fat digestion?
View Answer
Fatty acids and Glycerol.
Section 2: Respiration
Q11: Define respiration.
View Answer
Respiration is the process of breaking down food to release energy.
Q12: What is the chemical form of energy released during respiration?
View Answer
ATP (Adenosine Triphosphate).
Q13: List the end products of aerobic respiration.
View Answer
Carbon Dioxide (CO2), Water (H2O), and Energy.
Q14: Where in the cell does respiration take place?
View Answer
In the Mitochondria.
Q15: What substance is produced during anaerobic respiration in human muscles?
View Answer
Lactic acid.
Section 3: Transportation & Circulatory System
Q16: What is the biological definition of transportation?
View Answer
Transportation is the movement of food, oxygen, hormones, and wastes inside the body.
Q17: Name the three main components of the human circulatory system.
View Answer
1. Heart. 2. Blood. 3. Blood vessels.
Q18: How many chambers does the human heart have?
View Answer
Four chambers.
Q19: Which blood vessels carry oxygenated blood away from the heart?
View Answer
Arteries.
Q20: What is the function of White Blood Cells (WBC)?
View Answer
Immunity (protecting the body against diseases).
Q21: Which component of blood acts as the transport medium?
View Answer
Plasma.
Q22: Where does the exchange of materials between blood and cells occur?
View Answer
In the Capillaries.
Section 4: Metals, Non-Metals & Chemical Bonding
Q23: How do metals form positive ions (Cations)?
View Answer
By losing electrons.
Q24: What is the name of the negative ions formed by non-metals?
View Answer
Anions.
Q25: Define an Ionic Bond.
View Answer
An ionic bond is formed by the complete transfer of electrons from one atom to another.
Q26: State the electron configuration of a Sodium atom (Na).
View Answer
2, 8, 1.
Q27: What force holds oppositely charged ions together in an ionic compound?
View Answer
A strong electrostatic force of attraction.
Q28: Give the chemical formula for Sodium Chloride.
View Answer
NaCl.
Q29: What happens to a Chlorine atom when it becomes a Chloride ion (Cl–)?
View Answer
It gains one electron to complete its outer shell (2, 8, 8).
Q30: Identify the site where glucose is broken down to release energy.
View Answer
The Mitochondria.
| Enzyme / Juice | Target Food & Function | End Product |
|---|---|---|
| Salivary Amylase | Breaks down cooked Starch in the mouth. | Maltose |
| Pepsin / Renin | Digests Proteins in the acidic environment of the stomach. | Peptides / Polypeptides |
| Trypsin | Continues Protein digestion in the small intestine. | Amino Acids |
| Lipase | Breaks down Fats and Oils (Lipids). | Fatty Acids & Glycerol |
| Bile Juice | Emulsifies (breaks down) large fat globules into small droplets. | Emulsified Fats |
| LATEST EDUCATION STORIES |
| [display-posts posts_per_page="10" include_date="true"] |
| View All Breaking News → |


 2026 BECE Social Studies Projected Topics, Questions And Answers
2026 BECE Social Studies Projected Topics, Questions And Answers  Everything You Need to Know About Fugu, Batakari, and Northern Smock Types
Everything You Need to Know About Fugu, Batakari, and Northern Smock Types  2026 BECE 50 Mathematics Practice Questions With Answers And Solving Steps
2026 BECE 50 Mathematics Practice Questions With Answers And Solving Steps  2026 BECE Projected Mathematics Topics, Must-Know Formulas: Master These for Grade “1”
2026 BECE Projected Mathematics Topics, Must-Know Formulas: Master These for Grade “1”