Test Yourself With This INTEGRATED SCIENCE 2 & 1 NOW Before Day (2)
Test Yourself With This INTEGRATED SCIENCE 2 & 1 NOW Before Day (2)
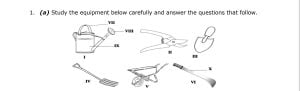
1. (a) Study the equipment below carefully and answer the questions that follow
i. What collective name is given to the equipment above?
ii. State three importance of these equipment in crop production.
iii. Identify the equipment labelled I, II, III, IV, V and VI.
iv. Name the parts labelled VII, VIII, IX and X.
v. State one use of each of the equipment above
vi. Give two general ways of maintaining the equipment.
(b) The diagrams below are illustrations of hazard symbols found in everyday life.
Study them carefully and use them to answer the questions that follow:
i. What does each symbol I, II, III, IV, V and VI represent?
ii. Identify one substance each that is associated with each of the symbols I,
II, III, IV and V.
iii. Name two places where the symbol VI can be found.
iv. Which of the symbol(s) is/are found on chemical containers?
v. State two importance of hazard symbols in everyday life.
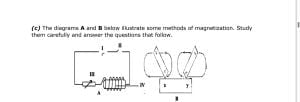
(c) The diagrams A and B below illustrate some methods of magnetization. Study
them carefully and answer the questions that follow.
i. Mention the methods of magnetization illustrated as A and B.
ii. Identify the parts labelled I, II, III and IV.
iii. Name the polarity of the ends x and y after the magnetization.
iv. Describe how you will test for the poles of x and y.
v. List two substances that can be made into a magnet.
vi. Give two precautions each that should be taken during each magnetization
process.
vii. Which of the two methods will produce a stronger magnet?
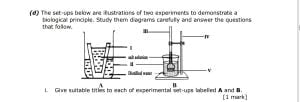
(d) The set-ups below are illustrations of two experiments to demonstrate a
biological principle. Study them diagrams carefully and answer the questions
that follow.
i. Give suitable titles to each of experimental set-ups labelled A and B.
ii. Name the parts labelled I, II, III, IV and V.
iii. Explain briefly the observation(s) that would be made if the two set-ups
are left to stand for two hours.
iv. What is/are the role(s) played by the parts labelled I and V in the
experiment?
v. Identify the biological principle being demonstrated in these experiments.
vi. State two ways each in which the biological principle above is beneficial
to:
(a) plants;
(b) animals.
SECTION B
2. (a) Explain the following terms associated with light energy:
(i) reflection of light;
(ii) refraction of light;
(iii) rectilinear propagation of light.
(b) The diagram below illustrates a scientific phenomenon. Study it carefully
and answer the questions that follow.
(i) What scientific phenomenon does the diagram illustrate?
(ii) Identify each part labelled I, II, q1 and q2.
(iii)State two everyday events that occur due to the phenomenon above.
(iv)What happens to the speed of light when it travels from air to glass?
(c) Explain how the streamlined body of a Tilapia enables it to live successfully
in an aquatic habit.
(d) (i) What is a fertilizer?
(ii) State four methods of fertilizer application.
(iii) Give two advantages of organic fertilizer over inorganic fertilizer.
3. (a) (i) What is a chemical compound?
(ii) State two differences between table salt (NaCl) and salt solution.
(iii) Write the chemical formula for each of the following chemical
compounds:
(α) ammonium hydroxide; (β) potassium chloride;
(γ) iron (II) chloride; (δ) carbon monoxide.
(b) Give one function each of the following organs in the digestive system of
humans:
(i) stomach; (ii) oesophagus; (iii) small intestines.
(c) (i) State the difference between a fuse and a resistor.
(ii) Name the colour codes for each of the following wires in an electric plug:
(α) live wire; (β) neutral wire; (γ) earth wire.
(d) (i) What is soil erosion?
(ii) Name two agents of soil erosion.
(iii) State two methods of controlling soil erosion. [3 marks]
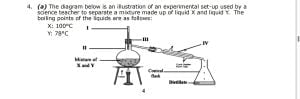
4. (a) The diagram below is an illustration of an experimental set-up used by a
science teacher to separate a mixture made up of liquid X and liquid Y. The
boiling points of the liquids are as follows:
X: 100°C
Y: 78°C
(i) What method of separation does the diagram represent?
(ii) Identify the parts labelled I, II, III and IV.
(iii) Which of the liquids X and Y would be collected first as the distillate and
why?
(iv)State the functions of the parts labelled I and IV.
(b)(i) Name the stages in the life cycle of mosquito.
(ii) State the four methods of controlling mosquitoes. [4 marks]
(c) Name one measuring instrument used to measure each of the following
physicals quantities:
(i) area of school garden; (ii) temperature of boiling alcohol;
(iii) weight of newborn baby; (iv)volume of milk.
(d) Give two examples each of the following:
(i) major plant nutrients; (ii) minor plant nutrients.
5. (a) (i) What is a simple machine?
(ii) Name four types of simple machines.
(iii) Explain how the efficiency of simple machines can be improved.
(b) (i) Distinguish between crop rotation and land rotation.
(ii) State three advantages of crop rotation over land rotation.
(c) Name two organs in each of the following human body systems:
(i) male reproductive system; (ii) female reproductive system;
(iii) respiratory system.
(d) State the compositions of each of the following alloys:
(i) bronze; (ii) brass;
(iii) solder; (iv) steel.
6. (a) (i) What is soil profile?
(ii) Name the four main horizons of a typical soil profile.
(iii) Which part of a typical soil profile is the richest in humus?
(iv) State two importance of the knowledge of soil profile to a farmer.
(b) (i) Distinguish between a cation and an anion.
(ii) Give two examples each of a cation and an anion.
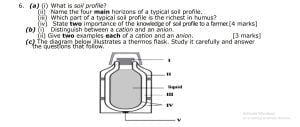
(c) The diagram below illustrates a thermos flask. Study it carefully and answer
the questions that follow.
(i) Identify the parts labelled I, II, III, IV and V.
(ii) Explain how the device reduces heat loss or gain by
(α) radiation (β) convection
(γ) conduction
(iii) Give one use of the thermos flask.
(d) You are provided with a fresh leaf plucked from a potted plant that was kept
in the sunlight for about 8 hours. Describe how you would test for the presence of
starch in the leaf.
SUPER MOCK EXAMINATION, SEPTEMBER 2022
FINAL MARKING SCHEME
INTEGRATED SCIENCE
Section A
[40 marks]
1. (a) (i) Name given to the equipment displayed: Farm tools
(ii) Importance of farm tools in crop production
– They make work easier and more convenient
– They increase productivity
– They reduce time spent on work
– They make farming more efficient
(iii) Identification of labelled parts:
I → watering can II → secateurs III → hand trowel
IV → garden fork V → wheelbarrow VI → cutlass
(iv) Names of labelled parts:
VII → handle VIII → holes/perforations
IX → can X → blade
(v) Uses of the farm tools:
– Watering can: used for watering crops
– Secateurs: cutting small branches of crops (pruning)
– Hand trowel: for earthing-up
– Garden fork: for loosening or cutting and turning over soil
– Wheelbarrow: transporting items in the farm
– Cutlass: for weeding
(vi) General ways of maintaining equipment:
– clean tools off soil particles after use
– use the tools for their right purpose
– oil or grease metal parts to prevent rusting
– keep them at cool and dry places, etc.
(b) (i) Names of labelled hazard symbols:
I → highly flammable/inflammable
II → toxic/poisonous
III → harmful/irritant
IV → corrosive
V → oxidizing
VI → no naked flame
(ii) Substances associated with the hazard symbols:
I → petrol, diesel, kerosene, LPG, butane, propane, etc.
II → mercury, lead, formaldehyde, DDT, etc.
III → sulphuric acid, sodium hydroxide, nitric acid,
IV → hydrogen peroxide, bromine, sulphuric acid, sodium hydroxide
V → bromine, ammonium perchlorate, chromic acid, hydrogen
peroxide, etc.
(iii) Places where VI can be found: petrol station, gas station, petrol tankers,
gas tankers, public places, etc.
(iv) Symbols found on chemical containers: I, II, III, IV and V.
(v) Importance of hazard symbols in everyday life
– they warn us against impending danger
– they prevent or reduce injuries
– they ensure safety, etc.
(c) (i) Methods of magnetization illustrated:
A → electric method/electromagnetism
B → double touch/stroke method
(ii) Identifying labelled parts:
I → Cell II → Switch/Key III → rheostat/variable resistor
IV → solenoid
(iii) Polarities of ends x and y after magnetization:
x → North y → South
(iv) How to test for the poles of x and y after magnetization: The south pole
of a known magnet is brought towards end x of the bar. Attraction indicates that end x
is a north pole.
(v) Substances that can be made into a magnet: iron, nickel, cobalt, steel, etc.
[any two for 1 mark, @ ½ mark each]
(vi) – Precautions to be taken in experiment A
– electric current should be made to flow in the same direction
– avoid fluctuations in electricity flow [any two for 1 mark]
– Precautions to be taken in experiment B
– the bar magnet should be placed on a flat surface
– after each stroke, the magnets should be lifted off the magnet and the
whole process restarted [any two for 1 mark]
(vii) Method A (electric method) will produce a stronger magnet than method
(d) (i) Title for set-up A: Experiment to demonstrate osmosis in living tissue.
Title for set-up B: Experiment to demonstrate osmosis in non-living tissue.
(ii) Names of labelled parts:
I → Yam/potato/cocoyam cup II → Beaker III → Thistle funnel
IV → Retort stand and clamp V → Cellophane paper
(iii) – Observation in set-up A: water would move by osmosis from the beaker
into the yam cavity. This makes the level of salt solution to rise and the level of
distilled water to fall.
– Observation in set-up B: Water moves from the beaker into the thistle
funny by osmosis. This makes the level of salt solution in the thistle funnel to rise and
the level of distilled water to fall.
(iv)Roles played by I and V: They serve as semi-permeable membrane.
(v) Biological principle being demonstrated: Osmosis
(vi) () Benefits of osmosis in plants:
– Plants absorb water from the soil by osmosis
– Movement of water from one plant cell to another.
[1 mark @ ½ mark each]
() Benefits of osmosis in animals:
– Absorption of water in the large intestine
– Selective re-absorption of water in the kidneys
– Movement of water from one animal cell to another.
SECTION B
2. (a) (i) Reflection of light: It is the bouncing back of light when it hits/falls on/strikes
a shiny or polished area.
(ii) Refraction of light: It is the change in direction and speed of light as it travels
from one medium to another medium of different optical densities.
(iii) Rectilinear propagation of light: It is the principle/property of light that
enables it to travel in a straight line.
(b) (i) Refraction of light.
(ii) I → Incident ray II → Refracted ray 1 → angle of incidence
2 → angle of refraction
(iii) Everyday events that occur due to refraction of light
– formation of mirage
– pools and ponds appear shallower due to refraction
– a stick in water appears bent due to refraction, etc.
(iv) When light travels from air to glass, its speed decreases/reduces.
(c) (i) The streamlined body of a Tilapia reduces resistance in water while they swim
forward. This makes them swim easier and faster in water. [2 marks]
(d) (i) Definition of fertilizer: It is a substance that is added to soil or crops to
improve its fertility. [1 mark]
(ii) Methods of fertilizer application: broadcasting, ringing method, side dressing,
foliar/sprinkling/spraying method, drilling, etc. [any four for 2 marks, @ ½ mark]
(iii) Advantages of organic fertilizer over inorganic fertilizer
– It not harmful to the environment
– It stays in the soil longer than inorganic fertilizer
– Often improves soil structure
– Improves drainage in the soil
– Relatively cheaper than inorganic fertilizer, etc.
[any two for 2 marks, @ ½ each]
3. (a) (i) Definition of chemical compound: It is a substance that is formed by the
chemical composition of two or more elements. [1 mark]
(ii) Differences between table salt (NaCl) and salt solution
(iii) () ammonium hydroxide: NH4OH
() potassium chloride: KCl
() iron (II) chloride: FeCl2
() carbon monoxide: CO
(b) (i) Stomach: It receives and stores food temporarily for further digestion.
(ii) Oesophagus: Transports food from mouth to the stomach.
(iii)Small intestine: This is the site for final digestion.
(c) (i) Difference between fuse and resistor: A fuse is a strip/wire of metal inserted in
an electric circuit which melts to break flow of current when the current rises beyond
Table salt (NaCl) Salt solution
It is a chemical compound It is a mixture
It cannot be separated It can be separated into its
components
Formation involves chemical
change
Formation involves physical
change
Components are in fixed ratio Components are in fixed ratio
Has a chemical formula Does not have a chemical
formula
a certain safe level. A resistor is an electric component that opposes the flow of
electric current in a circuit.
(ii) () live wire – red/brown
() neutral wire – black/blue
() earth wire – green and yelloW
(d) (i) Meaning of soil erosion: It is the removal/wearing away of the topsoil by
agents such as wind and water.
(ii) Agents of erosion: water, wind
(iii)Methods of controlling soil erosion
– Cover cropping
– Terracing
– Strip cropping
– Contour ploughing
– Use of windbreaks
– Keeping the soil moist, etc.
4. (a) (i) Method of separation: Simple distillation
(ii) Names of labelled parts:
I → thermometer II → round-bottomed flask III → cork
IV → condenser [2 marks, @ ½ mark each]
(iii) Liquid Y would be separated first because of its relatively lower boiling point.
(iv)Function of thermometer (I): measuring the temperature of the mixture
Function of condenser (IV): converts the vapour back to liquid
(b) (i) Stages of the life cycle of mosquito: Egg, Larva, Pupa, Adult/Imago
(ii) Methods of controlling mosquitoes:
– physical control method
– chemical control method
– biological control method
– genetic control method
(c) (i) measuring tape
(ii) thermometer
(iii)balance or scale
(iv)measuring cylinder, beaker, conical flask, burette, etc.
(d) (i) Major plant nutrient: nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium, calcium, magnesium,
sulphur.
(ii) Minor plant nutrient: boron, zinc, molybdenum, copper, manganese, chlorine,
nickel.
5. (a) (i) Simple machine: It is any tool that make work easier and faster.
(ii) Types of simple machines: Lever, Inclined plane and wedge, Pulley, Wheel
and axle, Screw, Gear.
(iii)Efficiency of a machine can be improved by reducing friction and
maintaining it appropriately.
(b) (i) Difference between crop rotation and land rotation: Crop rotation is the
system of farming in which a farmer grows different kinds of crops on the same piece
of land in a definite sequence or order whereas land rotation is the system of farming
in which a farmer farms on a piece of land for some time and leaves it to clear new
land when the old land becomes less fertile. The farmer does not move to the new
land with his settlement. [1 mark,
(ii) Advantages of crop rotation over land rotation
– It can be practised on a relatively smaller piece of land
– Land is not wasted
– Does not destroy virgin forests
– Improves soil structure
– Reduces soil erosion, etc.
(c) (i) Male reproductive system: testes, epididymis, vas deferens/sperm ducts,
prostate gland, Cowper’s gland, urethra, penis, etc.
(ii) Female reproductive system: ovaries, Fallopian tubes, uterus/womb, cervix,
vagina, vulva, etc.
(iii)Respiratory system: nostrils, nasal cavity, pharynx/throat, larynx,
trachea/windpipe, bronchus, bronchioles, alveolus,
(d) (i) Bronze: copper and tin
(ii) Brass: copper and zinc
(iii)Solder: lead and tin
(iv)Steel: iron and carbon
6. (a) (i) Meaning of soil profile: It is the vertical cross-section through the soil
showing the various layers or horizons.
(ii) Horizons of a typical soil profile: Topsoil (A-horizon), Subsoil (B-horizon),
Weathered rocks (C-horizon), Bedrock (D-horizon)
(iii)Richest in humus: topsoil (A-horizon)
(iv) Importance of knowledge of soil profile to farmer
– it enables the farmer to know the type of crops to grow
– it determines the types of tools to use
– it determines the type of fertilizer to use
– helps the farmer know the depth of the soil, etc.
(b) (i) Difference between cation and anion: A cation is a positively charged atom
formed when the atom loses electron(s) whereas an anion is a negatively charged
atom formed when the atom gains electron (s).
(ii) Examples of cation: potassium ion (K+), sodium ion (Na+), Magnesium ion
(Mg2+), Calcium ion (Ca2+), Zinc ion (Zn2+), Aluminium ion (Al3+), etc.
Examples of anion: chloride ion (Cl-), sulphide ion (S2-), Oxide ion (O2-),
Fluoride ion (F-), etc. [any two for 1 mark,
(c) (i) Names of labelled parts:
I → cork II → double-walled glass container III → vacuum
IV → silvered surfaces V → vacuum seal
(ii) How the device reduces heat loss or gain by:
() radiation: the shiny/silvered surfaces reduces heat gain or gain by radiation
() convection: the presence of vacuum
() conduction: the presence of vacuum and cork [3 marks, @ 1 mark each]
(iii) Uses of thermos flask: It keeps substances cold or hot for a longer time
(d) How to test for starch in leaf
– Leaf is boiled or put in boiling water for one minute to kill the cells
– Leaf is dipped in alcohol warmed in a hot water bath to decolorize it
– Leaf is washed in cold water to soften it to soften it
– Leaf is placed on a white tile and few drops of iodine solution are placed on
it. Appearance of blue-black coloration indicates the presence of starch.
Send Stories | Social Media | Disclaimer
Send Stories and Articles for publication to [email protected]
We Are Active On Social Media
WhatsApp Channel: JOIN HERE
2024 BECE and WASSCE Channel - JOIN HERE
Facebook: JOIN HERE
Telegram: JOIN HERE
Twitter: FOLLOW US HERE
Instagram: FOLLOW US HERE
Disclaimer:
The information contained in this post on Ghana Education News is for general information purposes only. While we endeavour to keep the information up to date and correct, we make no representations or warranties of any kind, express or implied, about the completeness, accuracy, reliability, suitability or availability with respect to the website or the information, products, services, or related graphics contained on the post for any purpose.





 How to buy UG Admission Voucher with Momo/Shortcode
How to buy UG Admission Voucher with Momo/Shortcode  Top 5 Universities in the Netherlands for Masters Studies
Top 5 Universities in the Netherlands for Masters Studies  John Mahama Lists Plans for Education Sector When he is Voted for
John Mahama Lists Plans for Education Sector When he is Voted for  The Poll Tax Ordinance of 1852
The Poll Tax Ordinance of 1852  Asogli State rejects renaming Ho Technical University after Ephriam Amu
Asogli State rejects renaming Ho Technical University after Ephriam Amu
This is Soo marvelous