2025 BECE Science (Practical) Revision Q & A Before Bed Time

Before you go to bed, take a look at the following: 2025 BECE Science (Practical) Revision Questions and Answers. Do not skip any of the following questions. At the end of each question, the answers have been provided to aid your effective learning.
2025 BECE Science (Practical) Revision Q & A Before Bed Time
SECTION A
[40 marks]
Answer all questions from this section.
Question 1
(a) Study the organisms below and answer the questions that follow
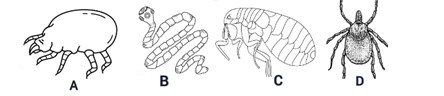
(i) Identify each of the organisms labeled A, B, C, and D (4 marks)
(ii) In which part of the body of hosts does each organism labeled live? (2 marks)
(iii) State one method of controlling each organism. (4 marks)
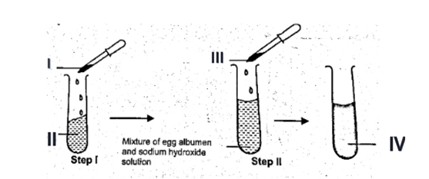
(b) The set-up below shows the chemical test for a food nutrient using Biuret method. Use it to answer the questions that follow.
(i) Name the parts labelled I, II, III and IV. (4 marks)
(ii) What food nutrient is being tested for in the set-up above? (1 mark)
(iii) What will be your conclusion at the end of the experiment? (2 marks)
(iv) Give three importance of the nutrient tested for, to the body. (3 marks)
(c) The set-up below is a demonstration by a basic 8 pupil using samples of the types of soil. Use it to answer the questions that follow.
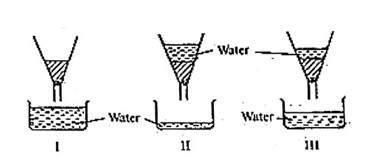
i. Suggest a suitable title for the experiment above. (2 marks)
ii. State three observations you can make from the set-up. (3 marks)
iii. Explain why the levels of water are different in the set-up. (3 marks)
iv. What conclusion could be drawn from the results of the experiment? (2 marks)
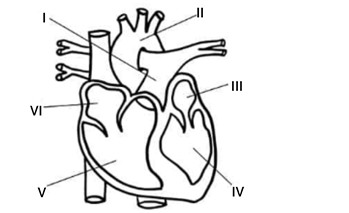
(d) Study the diagram below and answer the questions that follow.
i. Give an appropriate name for the diagram above. (1 mark)
ii. Name the parts labelled I to IV. (4 marks)
iii. What are the functions of V and VI? (2 marks)
iv. State three diseases of the diagram above. (3 marks)
SOLUTION FOR THE PRACTICAL QUESTIONS ABOVE
Now carefully look at the Answers to the 2025 BECE Science (Practical) Revision Questions above.
Question 1
(a) (i) Identification of organisms
• A – Mite
• B – Tapeworm
• C – Flea
• D – Tick 4 marks @ 1 mark each
(ii) Parts of the body of hosts where each organism labeled live
• Mite (A) – Skin
• Tapeworm (B) – Intestines
• Flea (C) – Skin
• Tick (D) – Skin 2 marks @ 0.5 mark each
(iii) Method of controlling each organism.
Mite (A) Control
• Maintain proper personal hygiene and regular bathing.
• Wash bedding and clothing with hot water.
• Use prescribed medicated creams or oral treatments. 1 mark each for any 1
Tapeworm (B) Control
• Cook meat and fish properly before consumption.
• Wash hands thoroughly before eating and after using the toilet.
• Avoid consuming contaminated food and water. 1 mark each for any 1
Flea (C) Control
• Regularly clean and vacuum pet bedding and living areas.
• Use flea control treatments on pets.
• Maintain proper yard sanitation to reduce flea breeding. 1 mark each for any 1
Tick (D) Control
• Keep grass and bushes trimmed to limit tick habitats.
• Use tick repellents on skin and clothing when in tick-prone areas.
• Check and remove ticks from the body and pets immediately after outdoor activities.
1 mark each for any 1
(b) (i) Names of the parts labelled I, II, III and IV.
I – Sodium hydroxide solution
II – Egg albumen
III – Copper sulphate
IV – Violet colour of the mixture 4 marks @ 1 mark each
(ii) Food nutrient is being tested for in the set-up above.
Protein 1 mark
(iii) Conclusion at the end of the experiment
The violet colour is an indication that protein is present in the egg albumen. 2 marks
(iv) Importance of the nutrient tested for (Protein), to the body.
• Body Building and Growth: Protein helps in the growth and repair of body tissues, especially muscles, skin, and organs. It’s essential for children, teenagers, and pregnant women.
• Enzyme and Hormone Production: Proteins are used to make enzymes and hormones that regulate body processes like digestion, metabolism, and growth.
• Immune System Support: Proteins help in the formation of antibodies, which fight off infections and protect the body from diseases. 4 marks @ 1 mark each
(c) i. Suggest a suitable title for the experiment above.
An experiment to demonstrate water holding capacity of sandy, loamy and clayey soil
OR
An experiment to demonstrate drainage ability of sandy, loamy and clayey soil
OR
An experiment to compare the porosity or permeability of sandy, loamy and clayey soil
2 marks for any 1
ii. State three observations you can make from the set-up.
• Sandy soil (diagram I) drains water quickly.
• Loamy soil diagram III) has moderate drainage ability.
• Clayey soil (diagram II) retains water for a longer time.
• Water infiltration is slower in clayey soil (diagram II) compared to sandy (diagram I) and loamy soil (diagram III).
1 mark each × any 3 = 3 marks
iii. Explain why the levels of water are different in the set-up.
The different levels of water in the experiment demonstrate the varying drainage abilities of sandy, loamy, and clayey soil due to differences in their porosity and permeability. Sandy soil (diagram I), with its larger particle size, allows water to drain quickly through its spaces. Loamy soil (diagram III), with a balanced mixture of sand, silt, and clay, has moderate drainage capacity. Clayey soil (diagram II), with its fine particles and compact structure, retains water for a longer time and drains slowly.
3 marks
iv. What conclusion could be drawn from the results of the experiment?
The conclusion drawn from the experiment could be that sandy soil (diagram I) has the highest drainage ability, loamy soil (diagram III) has moderate drainage ability, and clayey soil (diagram II) has the lowest drainage ability. This conclusion is based on the observation of the different water levels in each type of soil after water is added and allowed to drain.
2 marks
(d) i. Give an appropriate name for the diagram above.
Human/Mammalian heart 1 mark
ii. Name the parts labelled I to IV.
I – Pulmonary artery
II – Aorta
III – Left atrium
IV – Left ventricle 4 marks
iii. What are the functions of V and VI?
• V (Right ventricle)- The right ventricle pumps deoxygenated blood to the lungs for oxygenation. 1 mark
• VI (Right atrium) – The right atrium receives deoxygenated blood from the body and transfers it to the right ventricle. 1 mark
iv. State three diseases of the diagram above.
• Coronary artery disease (CAD)
• Hypertension (high blood pressure)
• Myocardial infarction (heart attack)
• Heart failure
• Arrhythmias (irregular heart rhythms) 1 mark × any 3 = 3 marks
We hope this 2025 BECE Science (Practical) Revision Questions and Answers goes a,png way to help you revise.





 Ghana’s First Aptitude Practice Online Service Launched by Education-News Consult
Ghana’s First Aptitude Practice Online Service Launched by Education-News Consult  Master Security Services Aptitude Test: Solve All Likely Questions on skulmanager.com/aptitude/test
Master Security Services Aptitude Test: Solve All Likely Questions on skulmanager.com/aptitude/test 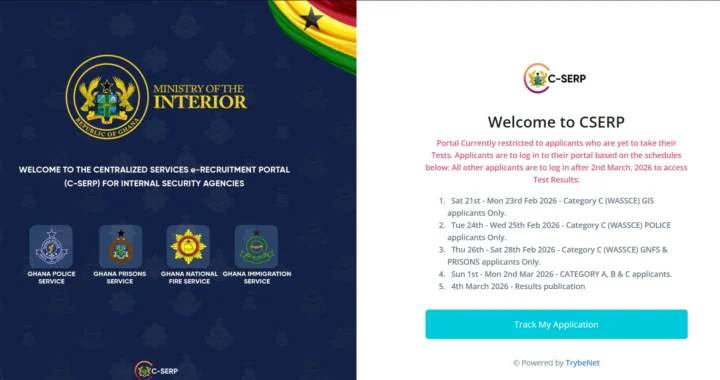 New Aptitude Test Dates for GIS, Police, and Prisons Recruitment 2026 Out
New Aptitude Test Dates for GIS, Police, and Prisons Recruitment 2026 Out
I want to buy 2025 BECE science questions and answers
SOrry we do not sell BECE WAEC questions yet to be administered becuase, w do not have them and we do not engage in illigality.
It’s very good