BECE Integrated Science Theory Questions And Answers For 2023 Candidates
Tuesday, 8th August, 2023 is the date for the Integrated Science paper during the 2023 BECE. We have compiled some likely theory and practical questions for the exams. Answers to these questions are also attached to this article.
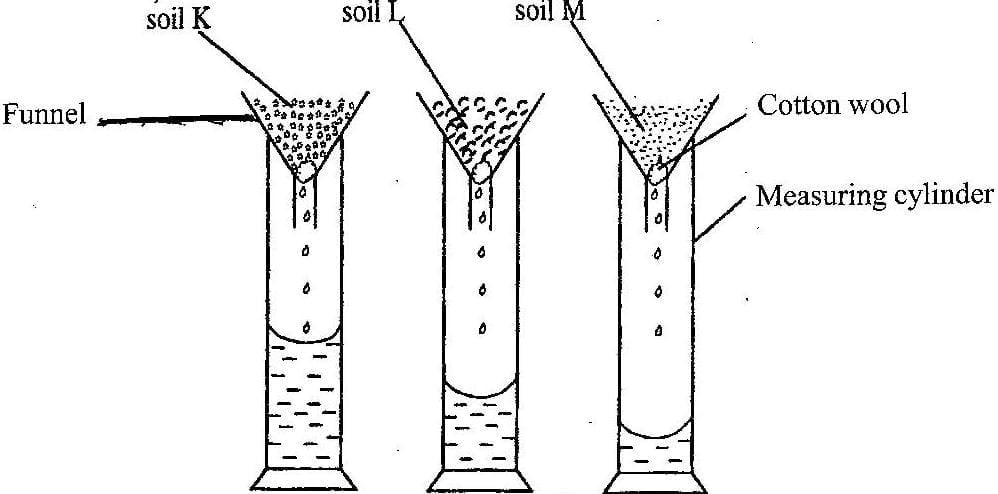
1. (a) The funnels in the diagram below contain equal amounts of different types of soils labelled K, L and M. Equal volumes of water were poured onto each soil at the same time and allowed to drain for 20 minutes.
Study the diagram and answer the questions that follow
(i) What is the aim of the experiment?
(ii) Which soil has the highest rate of drainage?
(iii) Which soil has the highest water retention capacity?
(iv) Which soil is most likely to lose water and dry faster after rainfall?
(v) Which soil is most likely to be waterlogged after rainfall.
(vi) Which of the soil types would be suitable for maize cultivation?
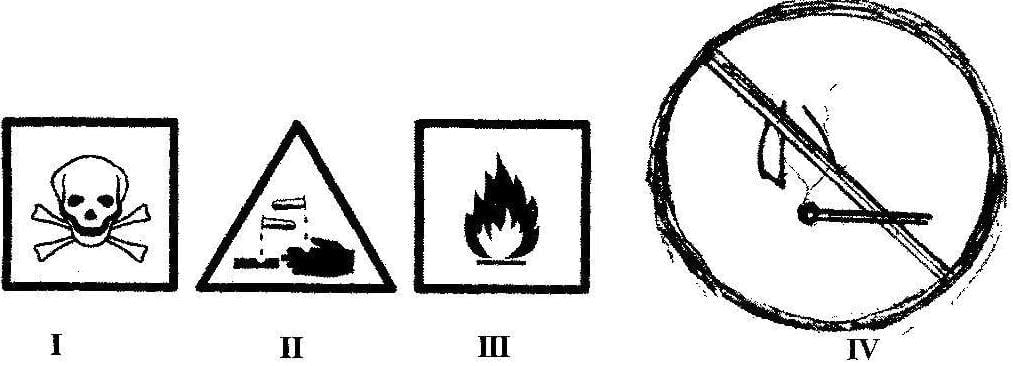
(b) The diagram below illustrates hazard symbols labelled I, II, III and IV.
Study the diagram carefully and answer the questions that follow.
(i) What does each of the symbols labelled I, II, III and IV represent?
(ii) Name one substance each that is associated with:
(α) I;
(β) II;
(γ) III.
(iii) Name a place where the hazard symbol labelled IV is often displayed
(iv) Which of the symbol(s) is / are found on chemical containers?
(c)The diagrams below are illustrations of devices used to do work easily
Study the diagrams and answer the questions that follow
(i) Give a general name for the devices.
(ii) Identify each of the devices labelled A, B, C and D.
(iii) Name the parts labelled I, II and III of device A when it is considered as a lever.
(iv) What does the arrow represent in the device labelled B?
(v) Name the type of work done with each of the devices labelled:
(α) C;
(β) D;
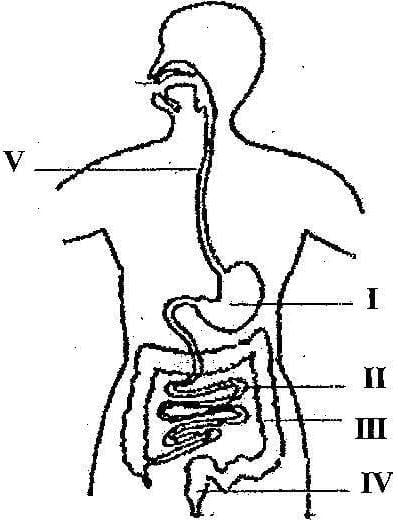
(d) The diagram below illustrates the digestive system in humans.
Study the diagram carefully and answer the questions that follow
(i) Name each of the parts labelled I, II, III, IV and V
(ii) Name the part(s) of the digestive system where
(α) digestion of food substances occur
(β) digested food is absorbed into the bloodstream
(iii) Name the end-products of the digestion that is absorbed into the bloodstream
2. (a) Name four weather measuring instruments.
(b) Name the stages in the life cycle of a mosquito.
(c) (i) List two properties of water
(ii) Explain why it is advisable to wash clothes with soft water
(d) State three ways in which soil profile is important.
3. (a) List three modes of heat transfer.
(b) (i) What is a deficiency disease?
(ii) Name three deficiency diseases in humans.
(c) State two ways in which each of the following factors cause depletion of soil resources:
(i) burning
(ii) leaching
(d) List three processes that can change matter from one state to another.
ANSWERS
1. (a) (i) The aim of the experiment.
To determine the drainage ability / water-holding capacity of the soils
(ii) Soil with the highest rate of drainage
Soil K
(iii) Soil with the highest water retention capacity.
Soil M
(iv) The soil most likely to lose water and dry faster after rainfall.
Soil K
(v) The soil most likely to be waterlogged after rainfall
Soil M
(vi) Which of the soil types would be suitable for maize cultivation? Soil L
(b) (i) What each of the symbols labelled I, II, III and IV represent
I – Danger
II – Corrosive
III – Highly inflammable / highly flammable
IV – No naked flame
(ii) One substance each that is associated with:
(α) I; DDT, Hydrogen cyanide, Salicylic acid
(β) II; Concentrated Inorganic acids, such as HCl, H2SO4, HNO3,
Concentrated inorganic bases, such as NaOH, KOH, Ca(OH)2
Household bleach
(γ) III. Petrol, Kerosene, LPG, Perfume, Insecticides, Alcohol
(iii) A place where the hazard symbol labelled IV is often displayed
Gas Filling stations, Storage places of combustible substances
(iv) Symbol(s) found on chemical containers I, II and III
(c) (i) General name for the devices. Simple machines
(ii) Identification of each of the devices labelled A, B, C and D.
A – Wheel barrow
B – Inclined plane
C – Pulley
D – Gear
(iii) The parts labelled I, II and III of device A when it is considered as a lever.
I – Effort
II – Load
III – Pivot
(iv) What the arrow represents in the device labelled B
Direction of effort / effort distance
(v) The type of work done with each of the devices labelled:
(α) C; Lifting objects
(β) D; moving a vehicle or parts of an engine efficiently
(d) (i) Names of the parts labelled I, II, III, IV and V
I – Stomach
II – Small intestines
III – Large intestines
IV – Rectum
V – Oesophagus / gullet
(ii) The part(s) of the digestive system where
(α) digestion of food substances occur
I and II
(β) digested food is absorbed into the bloodstream
(iii) The end-products of the digestion that is absorbed into the bloodstream
Amino acids, glucose, fatty acids and glycerol
2. (a) Four weather measuring instruments.
Barometer, rain gauge, anemometer, wind vane, hygrometer, sun dial / lightmeter
(b) The stages in the life cycle of a mosquito.
Egg stage, larva stage, pupa stage and adult stage
(c) (i) Two properties of water
• Colourless
• Odourless
• Tasteless
• Boils at 100°C
• Freezes at 0°C
(ii) Why it is advisable to wash clothes with soft water
It lathers better with soap, since it does not contain dissolved salts such as calcium carbonate, magnesium hydroxide and calcium sulphate.
There is no production of scum, therefore it makes washing easier and faster.
(d) Three ways in which soil profile is important.
• to determine the type of crop to grow
• to determine the most suitable farming system to use
• to determine the type / amount of fertilizer needed
• to determine the cultural practices to use
• to determine the type of tools / equipment to use
• to determine the cost of production
3. (a) Three modes of heat transfer. Conduction, convection and radiation
(b) (i) What a deficiency disease is
A disease that results from the lack or shortage of certain nutrients in the body of an organism
(ii) Three deficiency diseases in humans. Kwashiorkor, goiter, rickets, anaemia, scurvy, night blindness
(c) Two ways in which each of the following factors cause depletion of soil resources:
(i) burning
kills soil micro organism, such as nitrogen-fixing bacteria
makes the land bare, which results in soil erosion
causes faster evaporation of soil water
destroys soil nutrients
(ii) leaching
washes away water-soluble plant nutrients, especially nitrates and sulphur.
leads to soil acidity
affects the texture of the topsoil.
(d) Three processes that can change matter from one state to another.
Freezing
Condensation
Sublimation
Melting
Evaporation
Deposition
READ ALSO: British Council IELTS Prize 2023 | Win Up To 5,000 Pounds | Apply Here
Send Stories | Social Media | Disclaimer
Send Stories and Articles for publication to [email protected]
We Are Active On Social Media
WhatsApp Channel: JOIN HERE
2024 BECE and WASSCE Channel - JOIN HERE
Facebook: JOIN HERE
Telegram: JOIN HERE
Twitter: FOLLOW US HERE
Instagram: FOLLOW US HERE
Disclaimer:
The information contained in this post on Ghana Education News is for general information purposes only. While we endeavour to keep the information up to date and correct, we make no representations or warranties of any kind, express or implied, about the completeness, accuracy, reliability, suitability or availability with respect to the website or the information, products, services, or related graphics contained on the post for any purpose.




 How to buy UG Admission Voucher with Momo/Shortcode
How to buy UG Admission Voucher with Momo/Shortcode  Top 5 Universities in the Netherlands for Masters Studies
Top 5 Universities in the Netherlands for Masters Studies  John Mahama Lists Plans for Education Sector When he is Voted for
John Mahama Lists Plans for Education Sector When he is Voted for  The Poll Tax Ordinance of 1852
The Poll Tax Ordinance of 1852  Asogli State rejects renaming Ho Technical University after Ephriam Amu
Asogli State rejects renaming Ho Technical University after Ephriam Amu