Literature review in academic writing: Types, Importance and How to do a review

A literature review is an overview of the existing research on a particular topic. It is a critical evaluation and synthesis of the research studies and articles that have been published on a particular subject. The purpose of a literature review is to provide a comprehensive and up-to-date understanding of the existing knowledge, theories, and evidence related to a research question or topic.
A literature review is a key component of many research projects, including dissertations, theses, and research articles. It helps researchers to understand what has already been studied and what gaps in knowledge remain. By conducting a literature review, researchers can identify patterns and trends in the existing research, evaluate the quality of previous studies, and identify the strengths and limitations of previous research.
A literature review can be qualitative or quantitative in nature, depending on the research question and the type of studies being reviewed. A qualitative literature review may involve a narrative synthesis of the existing research, while a quantitative literature review may use meta-analytic techniques to combine the results of multiple studies.
A literature review is a comprehensive evaluation and synthesis of the existing research on a particular topic, aimed at providing a comprehensive understanding of the existing knowledge, theories, and evidence.
Importance of literature review in academic research
A literature review is a crucial component of academic research, and it is important for several reasons:
- Contextualization: A literature review provides the context and background information for a research study by summarizing the existing knowledge and theories related to the research topic.
- Identification of gaps in knowledge: By reviewing the existing literature, researchers can identify gaps in knowledge and areas where further research is needed.
- Synthesis of previous findings: A literature review synthesizes the findings of previous studies and identifies patterns and trends in the existing research, providing a comprehensive understanding of the topic.
- Development of new theories: By reviewing the existing literature, researchers can identify areas where new theories may be developed and contribute to the advancement of knowledge in the field.
- Justification of research: A literature review provides a foundation for the research study and helps to justify the need for the study by demonstrating the lack of existing knowledge in a particular area.
- Avoidance of duplication: A literature review helps to ensure that the research study is not duplicating previous work, and helps researchers to avoid conducting research that has already been done.
- Improved research methodology: A literature review can inform the design and methodology of a research study by highlighting the strengths and limitations of previous research and suggesting methods for improving future studies.
A literature review is an important component of academic research, providing context, identifying gaps in knowledge, synthesizing previous findings, justifying the research, avoiding duplication, and improving research methodology.
What are the types of literature reviews in academic research?
There are several types of literature reviews in academic research, including:
- Narrative review: A narrative review summarizes and synthesizes the existing research on a particular topic in a narrative format. It is often used to provide an overview of the existing knowledge in a field.
- Systematic review: A systematic review is a comprehensive and systematic evaluation of the existing literature on a particular topic. It is often used to synthesize the evidence and inform clinical practice or policy decisions.
- Meta-analysis: A meta-analysis is a statistical synthesis of the results of multiple studies that have been conducted on a particular topic. It is used to combine the results of individual studies to arrive at a more robust and precise estimate of the effect size.
- Scoping review: A scoping review is a type of systematic review that aims to map the existing research on a particular topic. It provides an overview of the existing knowledge and the extent, range, and nature of the research that has been conducted.
- Rapid review: A rapid review is a type of literature review that is conducted quickly, often in response to a pressing need for information. It is typically less comprehensive than a systematic review and may not be as rigorous.
- The integrative review: An integrative review synthesizes and integrates the findings of multiple studies and identifies patterns and trends in the existing research. It is often used to provide a comprehensive understanding of a particular topic or research area.
- Theoretical review: A theoretical review summarizes and evaluates the existing theories and models related to a particular topic. It is used to provide an overview of the current understanding of a particular theory or concept.
READ: How Can Paraphrasing Be Ethically Employed in Research Writing?
Dangers of a poorly done literature review
A poorly done literature review can have several dangers in academic research, including:
- Lack of validity: A poorly done literature review may not accurately represent the existing literature on a topic, which can compromise the validity of the research study.
- Bias: A poorly done literature review may be biased, either consciously or unconsciously, towards certain studies or outcomes, which can affect the accuracy and validity of the research findings.
- Lack of comprehensiveness: A poorly done literature review may not be comprehensive, potentially missing important studies or information related to the research topic.
- Inadequate justification of the research: A poorly done literature review may not provide a strong justification for the research, making it difficult to convince others of the importance and significance of the study.
- Duplication of previous research: A poorly done literature review may not identify previous research that has already been conducted, leading to duplication of effort and a waste of resources.
- Lack of rigor: A poorly done literature review may lack rigor, either in terms of the methodology used or in terms of the quality of the studies included, which can affect the credibility of the research.
- Poor recommendations: A poorly done literature review may not provide strong recommendations for future research, making it difficult to advance knowledge in the field.
READ: Factors to consider when choosing a research topic for a study
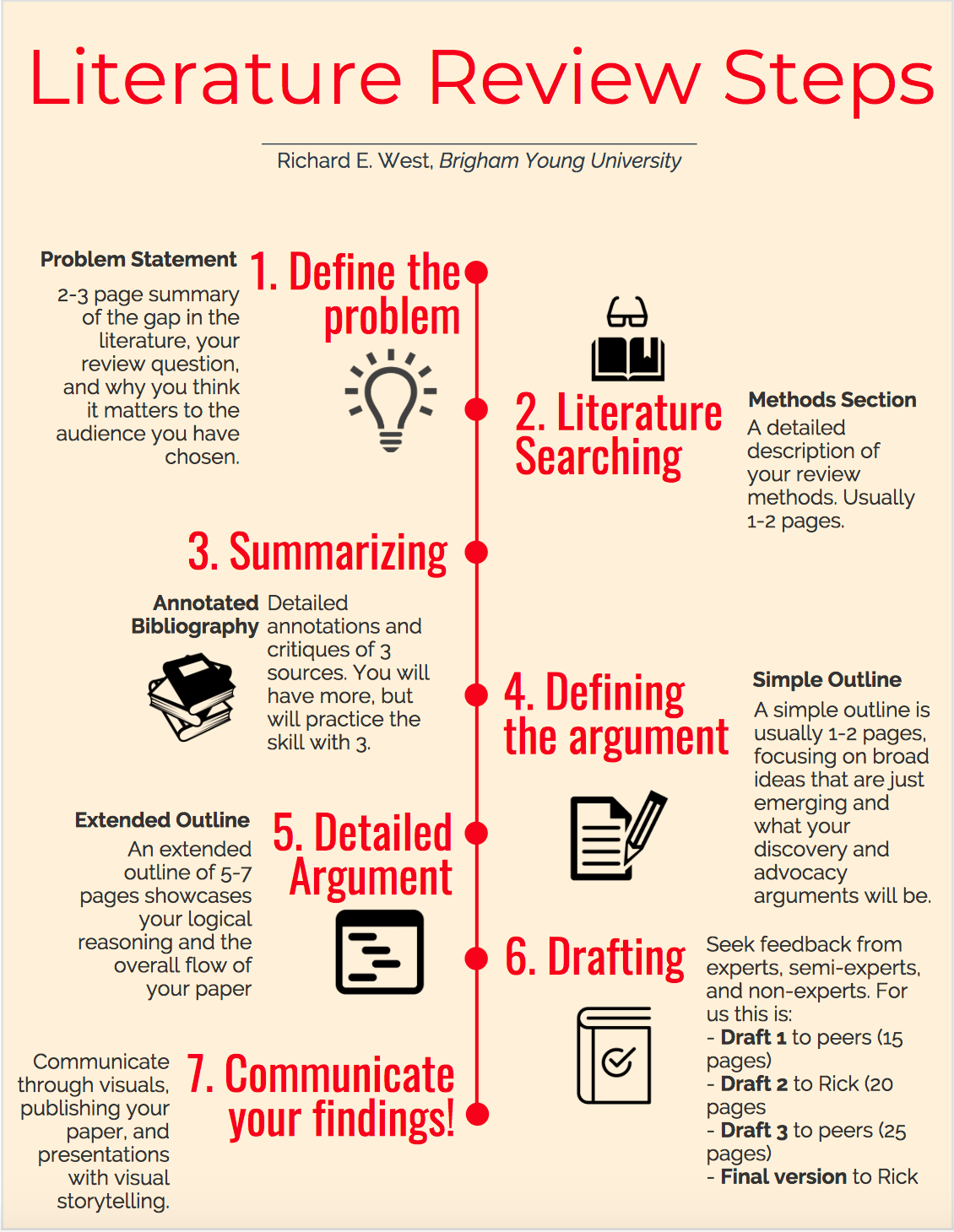
Steps that a good literature review goes through
A good literature review typically goes through the following steps:
- Define the research question: The first step in conducting a literature review is to define the research question. This helps to focus the literature review and ensure that the studies reviewed are relevant to the research question.
- Conduct a comprehensive search: The next step is to conduct a comprehensive search for studies that are relevant to the research question. This can involve searching databases such as PubMed, Google Scholar, and others, as well as manually searching reference lists and other sources of relevant studies.
- Evaluate the quality of the studies: Once relevant studies have been identified, they must be evaluated for quality. This can involve assessing factors such as the study design, sample size, and potential sources of bias. Only high-quality studies should be included in the literature review.
- Summarize and synthesize the findings: The next step is to summarize and synthesize the findings of the studies included in the literature review. This can involve organizing the findings by themes or categories and identifying patterns and trends in the data.
- Critically evaluate the existing literature: A good literature review must also critically evaluate the existing literature, including identifying gaps and limitations in the research, and pointing out any inconsistencies or contradictions in the findings.
- Draw conclusions and make recommendations: Based on the findings of the literature review, conclusions can be drawn and recommendations made for future research.
- Present the results: Finally, the results of the literature review must be presented in a clear and concise manner, typically as a chapter or section in a research paper or thesis.
READ: Qualitative and Quantitative Research: How different and similar are they?
In summary, a good literature review typically goes through several stages, including defining the research question, conducting a comprehensive search, evaluating the quality of the studies, summarizing and synthesizing the findings, critically evaluating the existing literature, drawing conclusions and making recommendations, and presenting the results.
Send Stories | Social Media | Disclaimer
Send Stories and Articles for publication to [email protected]
We Are Active On Social Media
WhatsApp Channel: JOIN HERE
2024 BECE and WASSCE Channel - JOIN HERE
Facebook: JOIN HERE
Telegram: JOIN HERE
Twitter: FOLLOW US HERE
Instagram: FOLLOW US HERE
Disclaimer:
The information contained in this post on Ghana Education News is for general information purposes only. While we endeavour to keep the information up to date and correct, we make no representations or warranties of any kind, express or implied, about the completeness, accuracy, reliability, suitability or availability with respect to the website or the information, products, services, or related graphics contained on the post for any purpose.



 GES To Query 42 Teachers In The Upper West Region; Here’s Why
GES To Query 42 Teachers In The Upper West Region; Here’s Why  Ministry of Education Denies Rebranding of Basic Schools
Ministry of Education Denies Rebranding of Basic Schools  GNPC Opens 2024 Scholarships Portal For New Applicants
GNPC Opens 2024 Scholarships Portal For New Applicants  Profile Of Kwabena Boateng, Ejisu MP Elect
Profile Of Kwabena Boateng, Ejisu MP Elect