UN Security Council Members (Permanent and non-permanent members)
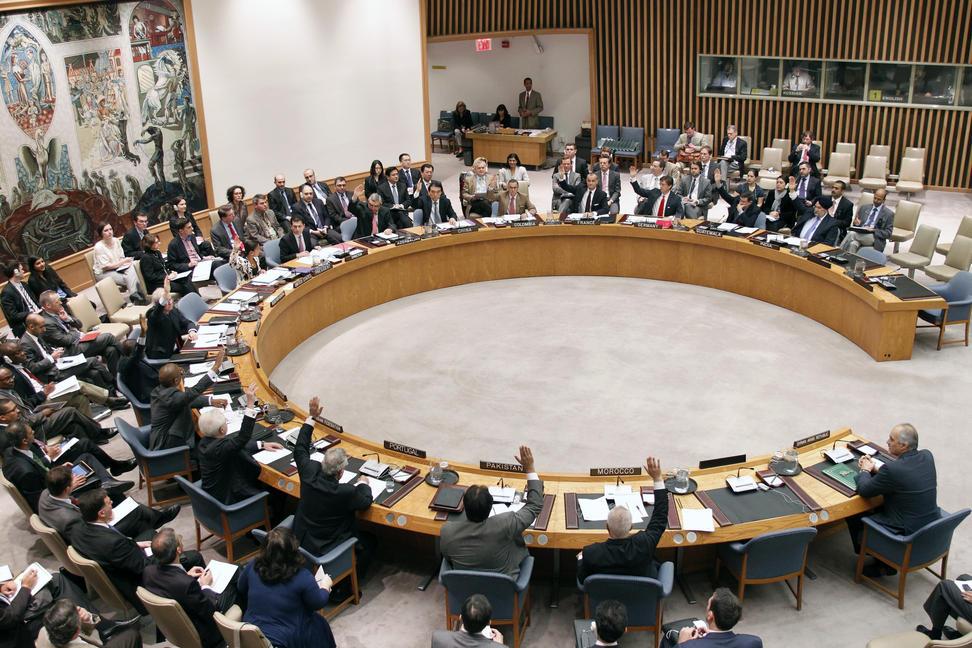

The UN Security Council is made up of two sets of countries known as permanent and non-permanent members.
The United Nations Security Council (UNSC) is a crucial organ of the United Nations responsible for maintaining international peace and security. Composed of 15 member states, including five permanent members (China, France, Russia, the United Kingdom, and the United States) and ten non-permanent members elected for two-year terms, the UNSC performs a range of functions to address conflicts, prevent aggression, and promote stability on a global scale.
- More than 50 UN member states have never been the members of the Security Council.
– A State which is a member of the United Nations but not of the Security Council may participate, without a vote, when they are subject of the discussion.
– Both Members and non-members of the United Nations, if they are parties to a dispute being considered by the Council, may be invited to take part, without a vote.
UN Security Council Members (Permanent)👇
🇨🇳 China
🇫🇷 France
🇷🇺 Russia
🇬🇧 United Kingdom
🇺🇸 United States
Ten non-permanent members (2-year term):
The current nonpermanent members are 10 in number.
🇦🇱 Albania
🇧🇷 Brazil
🇪🇨 Ecuador
🇬🇦 Gabon
🇬🇭 Ghana
🇯🇵 Japan
🇲🇹 Malta
🇲🇿 Mozambique
🇨🇭 Switzerland
🇦🇪 United Arab Emirates
READ: The World’s Most Expensive Places To Live in 2023
Functions of the United Nations Security Council (UNSC)
- Maintenance of International Peace and Security: The primary function of the UNSC is to maintain international peace and security. It identifies threats to peace, investigates disputes, and takes measures to resolve conflicts through peaceful means. This includes deploying peacekeeping missions, facilitating negotiations, and promoting dialogue between conflicting parties.
- Peacekeeping Operations: The UNSC has the authority to authorize the establishment of UN peacekeeping missions in areas of conflict. These missions are deployed to prevent the escalation of violence, protect civilians, facilitate humanitarian assistance, and support peace processes. The UNSC plays a vital role in shaping the mandates and strategies of these missions to address the specific challenges on the ground.
- Sanctions and Arms Embargoes: In cases where diplomatic efforts fail, the UNSC can impose sanctions or arms embargoes on countries or entities involved in threats to international peace and security. These measures aim to pressure parties into complying with international norms, cease hostilities, and engage in peaceful resolution of disputes.
- Authorization of Military Action: Under certain circumstances, the UNSC can authorize the use of military force to maintain or restore international peace and security. This includes actions to counter aggression, terrorism, or threats to international stability. Such authorizations provide legitimacy and collective international support for military interventions.
- Conflict Resolution and Mediation: The UNSC actively engages in conflict resolution and mediation efforts. It seeks to facilitate peaceful settlements by encouraging dialogue, brokering negotiations, and supporting mediation initiatives. The UNSC may appoint special envoys or establish ad hoc committees to assist in conflict resolution processes.
- International Law and Human Rights: The UNSC promotes adherence to international law and human rights norms. It ensures that conflicts and situations involving gross violations of human rights are addressed appropriately. The UNSC may refer cases to the International Criminal Court (ICC) or establish tribunals to hold individuals accountable for war crimes, genocide, or crimes against humanity.




 Terrorist Attack Ghanaian Tomato Traders in Burkina Faso
Terrorist Attack Ghanaian Tomato Traders in Burkina Faso  New Term 2 End of Term Question: Nursery to Grade 8 Exam Packs (2026)
New Term 2 End of Term Question: Nursery to Grade 8 Exam Packs (2026)  Why MTN Ghana’s Ghs399 Bundle is the Best Data Deal in 2026
Why MTN Ghana’s Ghs399 Bundle is the Best Data Deal in 2026  CAGD Salary Suspension 2026: Deadlines and Actions for Affected Staff
CAGD Salary Suspension 2026: Deadlines and Actions for Affected Staff