Different Grades of Petrol and Diesel And What Is Good For Your Car
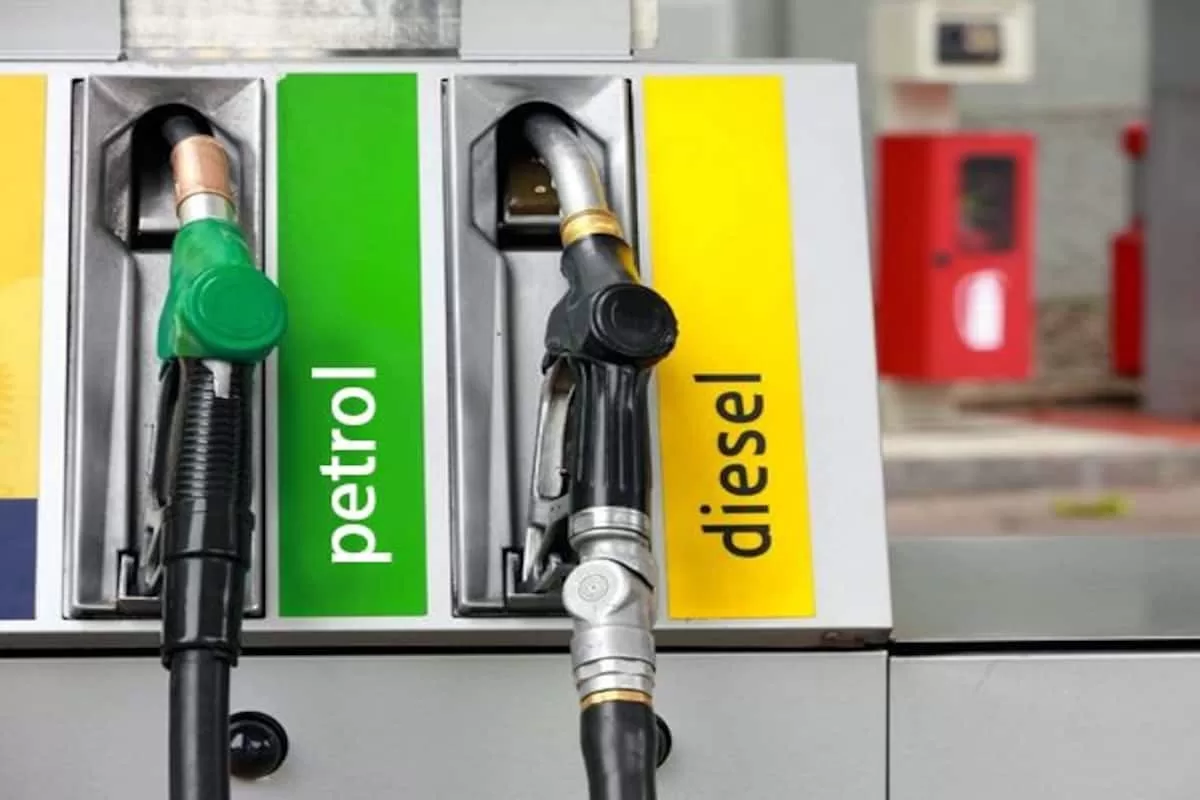

What is the best fuel for my car? What Fuel Grade Is Good For Your Car? Am I buying and using the right grades of Petrol and Diesel for my car?
Do You Know The Different Grades of Petrol and Diesel And What Is Good For Your Car? Or You Are The Kind Of Car Owner Or Driver Who Chooses Fuel Based On The Price Instead Or What Keeps Your Car Working Well and Prevents Frequent But Avoidable Visits to The Mechanics.
This post is worth yourme and reading effort as we give you expert advice
There are different grades of petrol and diesel at the various pumps because they have different octane ratings and cetane numbers. The octane rating measures a fuel’s resistance to knocking, while the cetane number measures a fuel’s ignition quality.
Different grades of petrol (often referred to as gasoline in some regions) and diesel exist to meet the diverse requirements of various types of vehicles and engines. These grades are typically categorized by their octane rating for petrol and cetane rating for diesel. Here’s why there are different grades and which ones are best for your car:
Octane rating
Knocking is a phenomenon that occurs when the fuel-air mixture in the engine ignites too early. This can cause damage to the engine. Higher octane fuels are less likely to knock than lower octane fuels.
Octane Rating for Petrol (Gasoline):
- Regular (87 octane): Regular petrol is suitable for most standard cars with lower compression engines. It is less expensive and works well for everyday driving.
- Mid-Grade (89-91 octane): Mid-grade petrol is designed for vehicles with higher compression engines, such as some sports cars and SUVs. It offers better performance and can prevent engine knocking in these high-performance vehicles.
- Premium (91+ octane): Premium petrol is formulated for high-performance and luxury vehicles with turbocharged or supercharged engines. These engines require higher octane levels to prevent knocking and maximize power output.
Cetane number
Cetane is a hydrocarbon that helps to ignite the fuel-air mixture in the engine. Higher cetane fuels ignite more easily than lower cetane fuels.
- Diesel #2: Diesel #2 is the most common type of diesel fuel. It is suitable for most diesel-powered vehicles, including trucks, buses, and some passenger cars. It offers a balance between performance and cost-effectiveness.
- Diesel #1: Diesel #1, also known as winter diesel, has a lower gel point and is designed for use in colder climates. It flows more easily at low temperatures, reducing the risk of fuel gelling or freezing in extreme cold.
- Ultra-Low Sulfur Diesel (ULSD): ULSD is a type of diesel fuel that has significantly reduced sulfur content. It is required for modern diesel engines equipped with advanced emissions control systems. Most diesel sold today is ULSD.
Which grades of petrol and diesel are best for your car?
The best grades of petrol and diesel for your car depend on its engine design. Some engines are designed to run on higher octane fuels, while others are designed to run on lower octane fuels. It is important to consult your car’s owner’s manual to determine which grades of petrol and diesel are recommended for your car.
Generally speaking, the following guidelines apply:
- Super petrol: Super petrol is recommended for cars with high compression engines, such as sports cars and luxury cars.
- Premium petrol: Premium petrol is a mid-grade fuel that is suitable for most cars.
- Regular petrol: Regular petrol is a lower-grade fuel that is suitable for older cars and cars with lower compression engines.
- Diesel: Diesel is recommended for diesel engines.
If you are unsure which grades of petrol and diesel are best for your car, it is always best to consult your mechanic.
Tips for choosing the right fuel for your car
- Avoid using low-grade fuels, as they can damage your engine.
- If you are driving in hot weather, use a higher octane fuel to help prevent knocking.
- If you are towing a heavy load, use a higher octane fuel to help prevent engine problems.
- If you are driving in a high-altitude area, use a higher octane fuel to help prevent knocking.
By following these tips, you can help to ensure that your car gets the best possible performance and fuel economy.
Send Stories | Social Media | Disclaimer
Send Stories and Articles for publication to [email protected]
We Are Active On Social Media
WhatsApp Channel: JOIN HERE
2024 BECE and WASSCE Channel - JOIN HERE
Facebook: JOIN HERE
Telegram: JOIN HERE
Twitter: FOLLOW US HERE
Instagram: FOLLOW US HERE
Disclaimer:
The information contained in this post on Ghana Education News is for general information purposes only. While we endeavour to keep the information up to date and correct, we make no representations or warranties of any kind, express or implied, about the completeness, accuracy, reliability, suitability or availability with respect to the website or the information, products, services, or related graphics contained on the post for any purpose.



 GES Opens Promotion Portal For Teaching Staff
GES Opens Promotion Portal For Teaching Staff  15 Year Old Girl Develops Anti-Sleep Device For Drivers
15 Year Old Girl Develops Anti-Sleep Device For Drivers  Emissions Levy Starts Today: Check How Much Car and Motor Owners Are Required To Pay
Emissions Levy Starts Today: Check How Much Car and Motor Owners Are Required To Pay 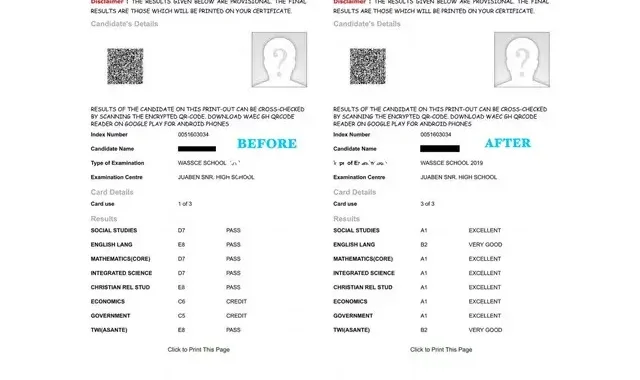 WASSCE Results Upgrading: Total Scam Or Something Worth Your Money?
WASSCE Results Upgrading: Total Scam Or Something Worth Your Money?  Update: No new uniforms or mass school repainting planned – MoE
Update: No new uniforms or mass school repainting planned – MoE  Why Nkrumah’s Face appeared on Guinea’s currency
Why Nkrumah’s Face appeared on Guinea’s currency  Controversies surrounding Ghana’s new public school uniform initiative
Controversies surrounding Ghana’s new public school uniform initiative